PELESTAT/PELECTRON Anti Static Agent
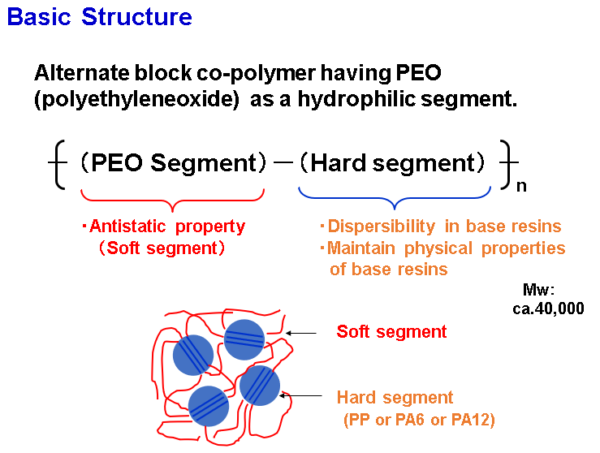
PELESTAT and PELECTRON are Inherently Dissipative Polymers (IDP) that are permanent antistatic additives when added to thermoplastic compounds. PELESTAT and PELECTRON are block copolymers that combine the static dissipation effectiveness of polyethylene oxide (PEO) with the physical properties of either polypropylene or polyamide.
The performance of PELESTAT/PELECTRON is superior to other antistatic additives for these reasons:
Protects against electrostatic discharge.
Will Not Wipe or Wash Off.
Works in DRY Environments
Light Color
Minimal Effect on Compound Physical Properties
No Contamination of Cleanroom Environments
Low Ionic Content, Low Outgassing




PELESTAT/PELECTRON WILL NOT WASH OFF OR WEAR OFF
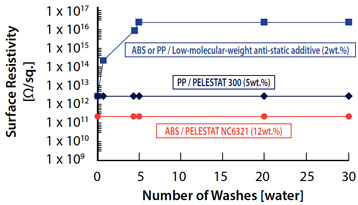
Maintaining Antistatic Properties 1
When a low molecular weight migratory-type antistatic agent is washed, the antistatic effect wears off. In the case of a permanent antistatic agent, the surface resistivity does not change even after repeated washings.
PELESTAT/PELECTRON WORK WELL IN WET OR DRY ENVIRONMENTS
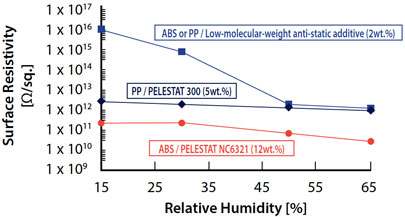
Maintaining Antistatic Properties 2
When a low molecular weight migratory-type antistatic agent is explored in dried air conditions like a clean room, the antistatic effect will weaken. In the case of a permanent antistatic agent, the surface resistivity does not change too much, even under 15% relative humidity.
ANTI STATIC PERFORMANCE AS A FUNCTION OF DOSAGEANTI-STATIC
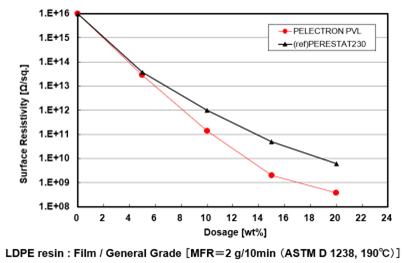
Adjusting Surface Resistivity
Pelestat and Pelectron enable resin parts to adjust surface resistivity in the broad range from 1016 to 108 Ω/sq.
The adjustment can be easy to control by dosages.
LEVELS OF ANTI STATIC PERFORMANCE
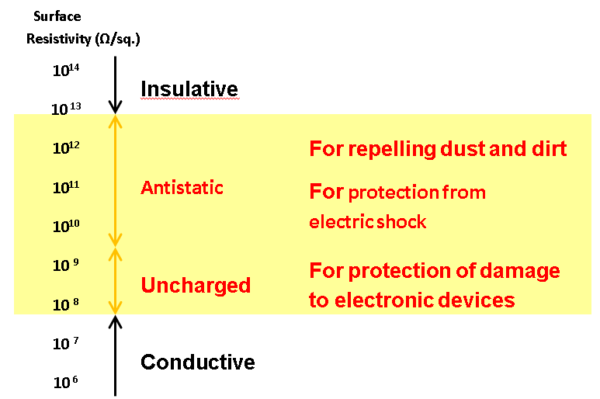
Superiority over Carbon-based Conductive Materials

Color Selectivity
Pelestat and Pelectron are clear to pale yellow pellet materials.
It has advantages over carbon-based conductive materials in homogeneous antistatic properties, low dust attraction, and impact resistance.
Basic Molecular Structure of PELESTAT & PELECTRON
SPECIFICATION
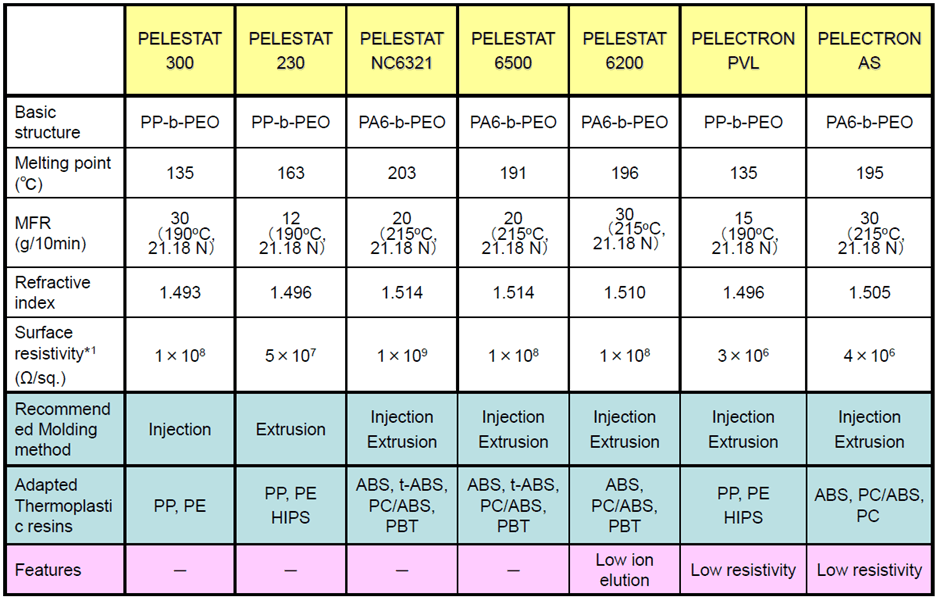
Applicable resins are not limited to the above examples. We have many experiences with broad resin materials. Feel free to contact us!
PELECTRON is the low surface resistivity grade. Check out about features of PELECTRON, especially focusing on precision electronic components like a chip.
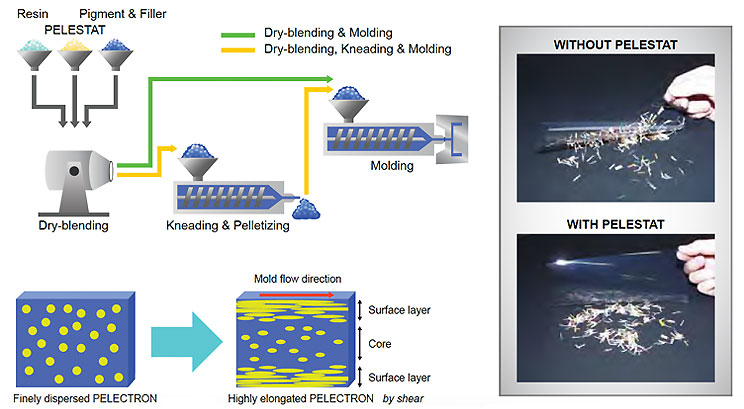
PROCESS FLOWCHART
Do you need more detailed information?
Do you want to try small samples?
Please contact us!
PELESTAT/PELECTRON Durability Demonstration Video:
Questions Asked About PELESTAT/PELECTRON and Other FAQs
We are all familiar with electrostatic discharge. It’s the “shock” you feel or spark you see when you shuffle across your carpeted living room on a winter morning and reach to touch the light switch. While painful, these shocks are not the worst side of electrostatic discharge. When handling semiconductors (computer chips) electrostatic discharge can destroy thousands of dollars of value in a split second. In ATEX applications in a mine or oil refinery or flour mill, electrostatic discharge can ignite an nightmarish inferno resulting in unimaginable death and destruction. Fortunately, electrostatic discharge can be avoided with the use of static dissipative materials which gradually “bleed off” (dissipate) any build up of static charge.
Among the materials most vulnerable to electrostatic discharge are everyday plastics. Virgin (uncompounded) plastics are inherently insulative. When PELESTAT or PELECTRON are added to them, plastics become dissipative. Since PELECTRON and PELESTAT are plastic additives, they must be added to plastic compounds with compounding equipment such as mixing extruders which employ powerful shear forces and high temperatures to disperse the additives evenly throughout the compound.
An antistatic additive is added to plastic compounds to eliminate problems caused by the buildup of static electric charge.
Static buildup in plastic parts can cause numerous problems. In addition to the painful shock we have all experienced, static charge attracts dust and dirt creating a dirty appearance. Also, static charge can cause thin film and sheet to stick together, reducing productivity. Finally, for plastic components used in flammable environments such as flour mills, mines, refineries and oil drilling operation, static charge can ignite an explosion.
Traditionally, antistatic additives are migratory in nature, meaning that they function by constantly bleeding or blooming to the plastic surface.
Since they function on the surface, these migratory antistatic additives are easily rubbed off or washed off, reducing their effectiveness and contaminating adjacent items. Also, they lose effectiveness over time, and since they must attract atmospheric moisture to function they do not work well in dry environments.
Static buildup in plastic parts can cause numerous problems. In addition to the painful shock we have all experienced, static charge attracts dust and dirt creating a dirty appearance. Also, static charge can cause thin film and sheet to stick together, reducing productivity. Finally, for plastic components used in flammable environments such as flour mills, mines, refineries and oil drilling operation, static charge can ignite an explosion.
Inherently dissipative polymers are also known as permanent antistatic additives. Since they are polymers, they do not migrate, do not wear off, do not wash off, offer permanent performance and are not dependent on atmospheric humidity
Most plastics are naturally insulative, meaning they do not conduct electricity and will hold a static electric charge. A static dissipative plastic is one which has been compounded with a suitable additive to allow a slow discharge of static electricity. A slow discharge of static electricity is essential in flammable environments in order to avoid sparking which can ignite an explosion.
The recommended test is ASTM D257. Results are expressed as “Ohms per square”. Higher numbers indicate higher electrical resistance and slower dissipation. Lower numbers mean lower electrical resistance and faster dissipation.
That depends. Traditional migratory antistatic additives must absorb moisture from the atmosphere in order to function. As a result they do not perform well in dry environments.
However, permanent antistatic additives do not rely on atmospheric moisture and this perform well in all environments, including the very dry.
The ATEX Directives (2014/34/EU & 1999/92/EC) are regulations of the European Union intended to protect employees from possible ignition of flammable or explosive atmospheres.
Examples of applicable industries would be oil/gas drilling operations, refineries, mines and powder processing operations such as sugar and flour mills. These directives require the dissipation of static electric charges.


