Ionic Liquid
Ionic liquid (IL) is a salt which exists as a liquid under 100°C. It has a wide range of application, including solvents, antistatic agents, absorbents and so on.
Ionic liquid (IL) is a salt which exists as a liquid under 100°C. It has a wide range of application, including solvents, antistatic agents, absorbents and so on.

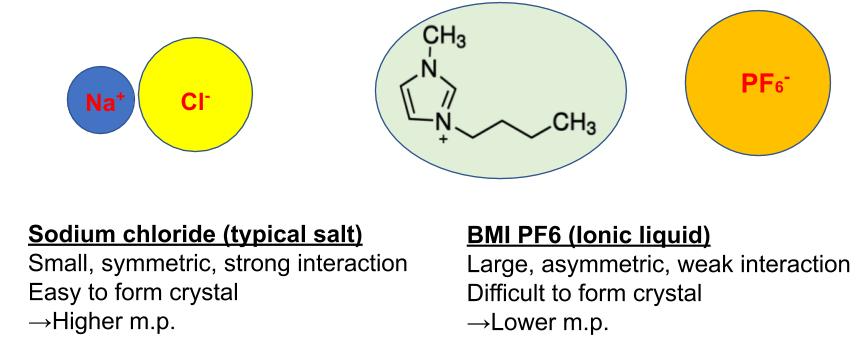
A typical ionic compound like NaCl has a higher melting point (m.p. 800C) due to its strong electrostatic interaction between Na+ ion and Cl- ion. In case of IL, the interaction between a cation and an anion is prevented by their bulkiness and asymmetricity. These features make IL to form a weak ion pair. This is the reason for IL’s low m.p. Due to IL’s unusual property, there are many applications as below.
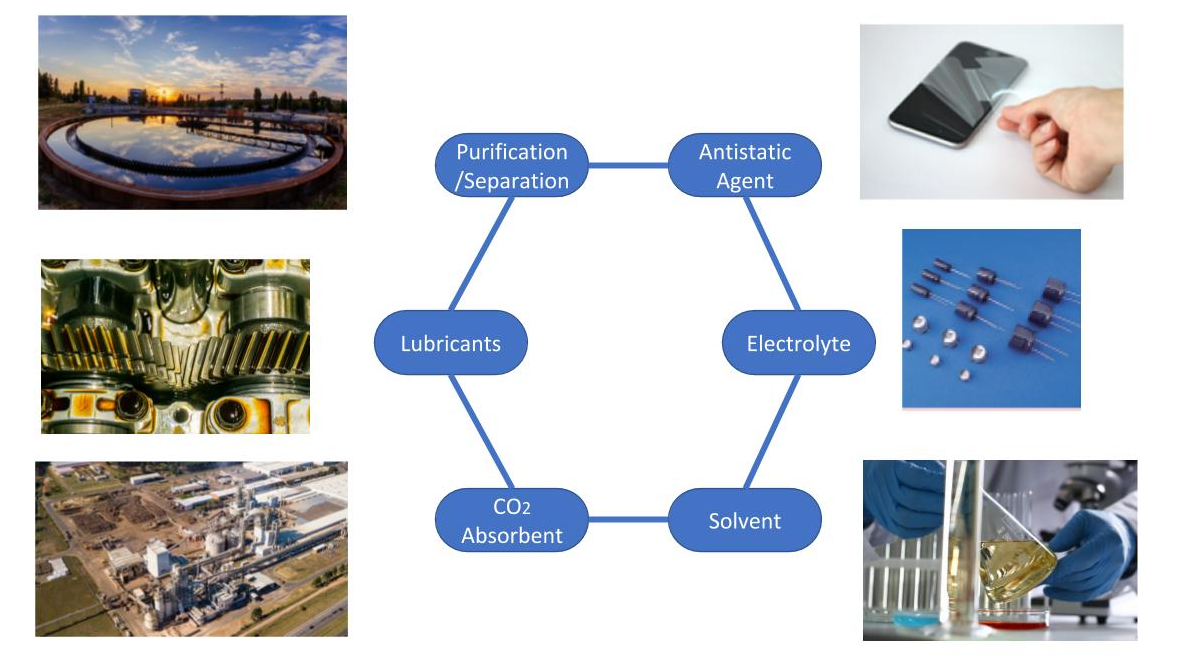
In recent years, Liquid Salts and Ionic Liquid have been studied in the following fields.
Liquid salts and ionic liquid can capture carbon dioxide(CO2) specifically by physical absorption. They are expected to be applied as a CO2 absorbent for Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS). *1
Since liquid salt has high ionic conductivity, it can be used in many electronic devices. For example, researchers at Linköping University have developed a thermoelectric generator.*2 On the other hand, scientists from Russia and Finnish have invented a transparent electrode by combining liquid salt and SWNT.*3
Ionic liquid salt is used for pretreatment lignocellulosis biomass prior to enzymatic hydrolysis. *4
There are several ways to synthesize ionic liquids. We manufacture them via carbonate method and ionic exchange method.
Molten salt is a salt which is melted by high temperature. For example, NaCl becomes molten salt at 801C. Ionic liquids are considered to be a kind of molten salt which is a liquid state under 100C.
Static interaction between cation and anion is weakened by their bulky structure. Asymmetric structure makes it difficult to crystalize so it can keep liquid state at ambient temperature.
It depends on its chemical composition, but generally speaking no.
Yes. But the conductivity is relatively low due to its high viscosity. If you need high conductivity, you have to dissolve it in low viscosity and high dielectric solvent like water or gamma butyrolactone.
Yes. IL’s vapor pressure is almost zero so it is considered to be a non VOC solvent.
An interaction between cation and anion makes vapor pressure lower or almost zero.
Yes, contact us.